1. What is EVA (Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate)?
EVA is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. It’s a versatile thermoplastic material known for its elasticity, softness, flexibility, toughness, and clarity. The percentage of vinyl acetate (VA) in the copolymer significantly influences its properties, with higher VA content generally leading to increased flexibility, adhesion, and lower melting points.
2. What are the key properties of EVA that make it useful in various applications?
EVA’s desirable properties include:
- Flexibility and Elasticity: Similar to rubber, but processable like thermoplastics.
- Toughness and Impact Strength: Good resistance to impact even at low temperatures.
- Clarity and Gloss: Can be formulated for transparent or translucent applications.
- Adhesion: Excellent adhesion to a wide range of substrates.
- Low-Temperature Toughness: Retains flexibility and impact strength in cold environments.
- Chemical Resistance: Good resistance to many chemicals, oils, and greases.
- UV Resistance: Can be formulated with UV stabilizers for outdoor applications.
- Processability: Easy to process using standard thermoplastic techniques like extrusion, injection molding, and blow molding.
3. What are some common applications of EVA?
EVA is used in a vast array of products, including:
- Footwear: Midsole foams, outsoles, insoles, and sandals.
- Packaging: Films, hot melt adhesives, seals, and caps.
- Wire and Cable: Insulation and jacketing.
- Automotive: Interior components, gaskets, and seals.
- Medical: Tubing, bags, and disposable medical devices.
- Sporting Goods: Protective gear, grips, and mats.
- Solar Panels: Encapsulants for photovoltaic cells.
- Construction: Adhesives, sealants, and roofing membranes.
- Toys and Crafts: Foam sheets, doll parts, and modeling clay.
4. What is EVA compounding?
EVA compounding is the process of blending EVA resin with various additives to modify its properties and tailor it for specific applications. This involves carefully selecting and combining different ingredients to achieve desired characteristics like color, hardness, flame retardancy, UV stability, processability, and more.
5. Why is compounding necessary for EVA?
While neat EVA has good inherent properties, compounding allows manufacturers to:
- Customize Properties: Achieve specific performance requirements (e.g., higher rigidity, better flow, increased UV resistance).
- Improve Processing: Enhance ease of processing during manufacturing (e.g., reduce cycle times, improve surface finish).
- Add Functionality: Introduce new features like flame retardancy, antimicrobial properties, or conductivity.
- Coloration: Add pigments or dyes to achieve desired colors.
- Reduce Costs: Incorporate fillers to lower material costs while maintaining acceptable performance.
6. What are the typical components used in EVA compounding?
Common additives used in EVA compounding include:
- Fillers: Calcium carbonate, talc, fumed silica, carbon black (for reinforcement, cost reduction, or specific properties like conductivity).
- Plasticizers: To increase flexibility and processability.
- Stabilizers:
- UV Stabilizers: To prevent degradation from sunlight exposure.
- Antioxidants: To prevent thermal degradation during processing and service life.
- Flame Retardants: Halogenated or halogen-free compounds to improve fire resistance.
- Colorants: Pigments or dyes for aesthetic purposes.
- Processing Aids: Lubricants, flow enhancers to improve melt flow and reduce friction during processing.
- Cross-linking Agents (Peroxides): For creating cross-linked EVA (XLPE or foamed EVA) which enhances heat resistance, compression set, and mechanical strength.
- Blowing Agents: For creating foamed EVA (e.g., azodicarbonamide for footwear midsoles).
- Adhesion Promoters: To improve bonding to other substrates.
- Antimicrobial Agents: To inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi.
7. What are the common compounding methods for EVA?
The most common methods for compounding EVA are:
- Twin-Screw Extrusion: Highly efficient for continuous compounding, offering excellent mixing and dispersion of additives.
- Internal Mixers (Banbury Mixers): Batch processes, ideal for high-viscosity formulations and achieving good dispersion. Often used for initial mixing before further processing.
- Single-Screw Extrusion: Can be used for simpler compounding tasks, but less effective for complex formulations or high filler loadings compared to twin-screw.
8. What are some challenges in EVA compounding?
Challenges can include:
- Dispersion of Additives: Ensuring uniform distribution of fillers, pigments, and other additives to achieve consistent properties.
- Thermal Stability: Preventing degradation of EVA or additives due to high temperatures during processing.
- Rheology Control: Managing the melt flow behavior to optimize processing and final product quality.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Minimizing emissions from certain additives, especially during foaming processes.
- Odor: Some additives or degradation products can contribute to undesirable odors.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Balancing desired properties with the cost of additives and processing.
9. What is the role of vinyl acetate content in EVA compounding?
The vinyl acetate (VA) content is crucial:
- Low VA (<10%): More like polyethylene, higher crystallinity, stiffer, less flexible, good barrier properties.
- Medium VA (10-25%): Good balance of flexibility, toughness, and adhesion. Common for films, adhesives, and footwear.
- High VA (>25%): More rubbery, excellent flexibility, adhesion, and clarity, lower melting point. Used in hot melt adhesives, solar encapsulants.
Compounding formulations will vary significantly depending on the VA content of the base EVA resin.
10. What quality control measures are important in EVA compounding?
Rigorous quality control is essential and often includes testing for:
- Melt Flow Index (MFI): To assess processability.
- Density: To ensure consistent formulation.
- Hardness (Shore A/D): To confirm mechanical properties.
- Tensile Strength and Elongation at Break: To measure mechanical performance.
- Color and Gloss: For aesthetic consistency.
- Ash Content: To determine filler loading.
- Specific Gravity: Another measure of density.
- Thermal Properties (DSC, TGA): For melting point, degradation temperature, and composition analysis.
- VOC Content: Especially for certain applications like automotive or medical.
Role of QC in EVA Chemical and Compounding Section: 20 FAQs
1. What is the primary role of QC in the EVA chemical and compounding section? Answer: The primary role of QC is to ensure that all raw materials, in-process materials, and finished EVA compounds meet predefined quality specifications, ensuring product consistency, performance, and customer satisfaction.
2. Why is QC particularly important in EVA compounding? Answer: EVA compounding involves blending various chemicals (EVA resin, additives, fillers, pigments). QC is crucial to ensure proper dispersion, homogeneity, consistent mechanical properties, and the absence of contaminants, which directly impact the final product’s functionality and appearance.
3. What types of raw materials does QC inspect for EVA compounding? Answer: QC inspects EVA resin (MFI, VA content), various additives (e.g., cross-linking agents, antioxidants, UV stabilizers), fillers (e.g., calcium carbonate, talc), pigments, and processing aids.
4. What are some key tests performed by QC on incoming EVA resin? Answer: Key tests include Melt Flow Index (MFI) to assess flowability, Vinyl Acetate (VA) content to determine flexibility and adhesion, density, and often visual inspection for contaminants.
5. How does QC ensure the quality of additives used in EVA compounding? Answer: QC verifies Certificates of Analysis (CoA) from suppliers, performs identity tests (e.g., FTIR, melting point), checks for purity, moisture content, and verifies dosage accuracy for critical additives.
6. What in-process checks does QC conduct during EVA compounding? Answer: In-process checks include monitoring temperature profiles, screw speed, pressure, and performing periodic sampling for visual inspection, melt flow rate, and sometimes preliminary mechanical tests to catch deviations early.
7. How does QC prevent cross-contamination in the compounding section? Answer: QC implements strict procedures for material handling, equipment cleaning protocols between batches, dedicated storage areas for different materials, and proper labeling to prevent cross-contamination.
8. What analytical techniques does QC commonly use for EVA compounds? Answer: Common techniques include Melt Flow Rate (MFR), Density, Shore Hardness, Tensile Strength, Elongation at Break, Tear Strength, Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) for melting point/crystallinity, and Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) for filler content.
9. What is the significance of Melt Flow Rate (MFR) testing for EVA compounds? Answer: MFR indicates the processability of the EVA compound. QC ensures MFR is within the specified range to guarantee consistent flow during downstream processing (e.g., extrusion, injection molding).
10. How does QC verify the color consistency of pigmented EVA compounds? Answer: QC uses colorimeters or spectrophotometers to measure color parameters (Lab* values) and compare them against established standards. Visual assessment under controlled lighting is also performed.
11. What role does QC play in troubleshooting production issues in the compounding section? Answer: QC analyzes non-conforming batches, identifies potential root causes (e.g., incorrect raw material, processing parameter deviation), and provides data to assist production in rectifying issues.
12. How does QC ensure the homogeneity of EVA compounds? Answer: QC assesses homogeneity through visual inspection for specks or unmixed material, and by performing mechanical tests on multiple samples from different parts of a batch to check for consistent properties.
13. What is a “Certificate of Analysis” (CoA) and how does QC use it? Answer: A CoA is a document from a supplier detailing the specifications and test results of a material. QC uses CoAs to verify incoming material quality and often performs confirmation testing.
14. How does QC manage non-conforming materials or batches? Answer: Non-conforming materials are isolated, clearly labeled, and quarantined. QC initiates a Material Review Board (MRB) process to determine disposition (rework, regrind, scrap, or special use approval).
15. What are the calibration requirements for QC equipment in an EVA plant? Answer: All QC testing equipment must be regularly calibrated according to manufacturer specifications and established schedules to ensure accurate and reliable test results. Calibration records are meticulously maintained.
16. How does QC contribute to process optimization in EVA compounding? Answer: By providing consistent and reliable data on material properties and performance, QC helps identify areas for process improvement, such as optimizing mixing parameters or additive concentrations.
17. What documentation does QC maintain in the EVA compounding section? Answer: QC maintains records of incoming material inspections, in-process checks, finished product test results, calibration records, non-conformance reports, and Certificates of Conformance for outgoing products.
18. What is the importance of retaining samples in the QC lab for EVA compounds? Answer: Retained samples (retain samples or retain archive) serve as a reference for future investigations, customer complaints, or to re-test if there are any doubts about past production.
19. How does QC ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations? Answer: QC stays updated on relevant industry standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO) and regulations (e.g., REACH, FDA for specific applications) and ensures that testing methods and product specifications align with these requirements.
20. What is the ultimate goal of QC in the EVA chemical and compounding section? Answer: The ultimate goal is to consistently deliver high-quality EVA compounds that meet or exceed customer expectations, ensuring product reliability, safety, and enhancing the company’s reputation.
Role of QA in EVA Chemical and Compounding Section
General Role of QA
- Q: What is the primary role of Quality Assurance (QA) in an EVA chemical and compounding section?
- A: The primary role of QA is to ensure that all products, processes, and systems consistently meet pre-defined quality standards, regulatory requirements, and customer specifications. This involves preventing defects rather than just detecting them.
- Q: How does QA contribute to product consistency in EVA compounding?
- A: QA contributes by establishing and enforcing strict quality control points throughout the entire process, from raw material inspection to final product testing. This includes monitoring process parameters, calibrating equipment, and ensuring adherence to Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs).
- Q: What is the difference between Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) in this context?
- A: QA focuses on preventing defects by setting up robust systems and processes, while QC focuses on detecting defects through testing and inspection of materials and finished products. In practice, they are often intertwined.
- Q: Why is QA particularly important in the chemical and compounding industry, especially for EVA?
- A: QA is crucial due to the variability of raw materials, the complexity of chemical reactions, and the need for precise formulations to achieve specific properties in the final EVA product. Inconsistent quality can lead to significant product failures and safety issues.
Raw Material Management
- Q: What is QA’s role in the inspection and approval of incoming raw materials for EVA compounding?
- A: QA is responsible for establishing specifications for all incoming raw materials (EVA resins, additives, pigments, etc.), conducting thorough inspections upon arrival, verifying Certificates of Analysis (CoAs), and performing necessary in-house testing to ensure they meet the required quality standards before release for production.
- Q: How does QA handle non-conforming raw materials?
- A: QA initiates a non-conformance procedure, quarantines the material, investigates the root cause, and determines appropriate corrective actions, which may include returning the material to the supplier, re-testing, or disposition based on risk assessment.
Process Control and Monitoring
- Q: How does QA ensure the quality of the compounding process itself?
- A: QA develops and monitors critical process parameters (e.g., temperature profiles, screw speed, feeding rates, pressure) for extruders and mixers. They establish statistical process control (SPC) limits and ensure operators are trained to adhere to these parameters.
- Q: What documentation does QA typically manage in an EVA compounding section?
- A: QA manages a wide range of documentation, including SOPs, batch records, material specifications, test methods, equipment calibration records, deviation reports, non-conformance reports, and Certificates of Analysis (CoAs) for finished products.
- Q: What is the significance of “batch records” from a QA perspective in EVA compounding?
- A: Batch records are critical as they provide a complete history of each production batch, detailing raw materials used, processing conditions, in-process test results, and final product release information. They are essential for traceability and investigations.
- Q: How does QA ensure equipment calibration and maintenance contribute to product quality?
- A: QA establishes and oversees a robust equipment calibration and preventative maintenance program. Properly calibrated and maintained equipment ensures accurate process control and reliable test results, directly impacting product consistency and quality.
In-Process and Finished Product Testing
- Q: What types of in-process tests does QA typically oversee in EVA compounding?
- A: In-process tests can include melt flow index (MFI), density, color consistency, and visual inspection for homogeneity, ensuring the compound is developing as expected before final product formation.
- Q: What are some key final product tests QA performs or oversees for EVA compounds?
- A: Final product tests often include MFI, density, hardness (Shore A/D), tensile strength, elongation at break, tear strength, color measurements, and potentially specialized tests like Vicat softening point or heat distortion temperature, depending on the application.
- Q: How does QA ensure the accuracy and reliability of laboratory testing?
- A: QA ensures accuracy through regular calibration of lab equipment, participation in inter-laboratory comparison programs (round robins), using certified reference materials, and validating test methods.
Compliance and Continuous Improvement
- Q: What role does QA play in ensuring regulatory compliance for EVA products?
- A: QA ensures compliance with relevant industry standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO), regulatory requirements (e.g., REACH, RoHS if applicable), and customer-specific regulations. This includes maintaining necessary certifications and documentation.
- Q: How does QA handle customer complaints related to EVA products?
- A: QA leads the investigation of customer complaints, identifies the root cause using tools like 5 Whys or Fishbone diagrams, implements corrective and preventive actions (CAPAs), and communicates findings back to the customer.
- Q: What is a CAPA, and how is it utilized by QA?
- A: CAPA stands for Corrective Action and Preventive Action. QA uses CAPAs to address identified non-conformities or quality issues by implementing actions to eliminate the cause of the problem (corrective) and prevent its recurrence (preventive).
- Q: How does QA contribute to continuous improvement in the EVA chemical and compounding section?
- A: QA drives continuous improvement by analyzing quality data, identifying trends, leading root cause analyses, implementing CAPAs, participating in process optimization projects, and conducting internal audits to find areas for enhancement.
- Q: What is the importance of internal audits from a QA perspective?
- A: Internal audits are crucial for QA to objectively assess the effectiveness of the Quality Management System (QMS), identify non-conformities or areas for improvement, and ensure ongoing compliance with established procedures and standards.
- Q: How does QA ensure traceability within the EVA compounding process?
- A: QA implements robust traceability systems that link raw material batches to specific production batches and ultimately to finished product lots. This allows for quick identification and isolation of affected products in case of a quality issue.
- Q: What training responsibilities does QA have for personnel in the EVA compounding section?
- A: QA ensures that all personnel involved in critical quality activities receive adequate training on SOPs, test methods, quality policies, and the importance of adhering to quality standards. They also maintain training records.
FAQs: Role of Chemist and Production Team in EVA Chemical and Compounding Section
General Roles & Responsibilities
- Q: What is the primary role of a Chemist in the EVA chemical and compounding section?
- A: The primary role of a Chemist is to focus on research, development, quality control, and technical support related to the chemical properties, formulation, and performance of EVA polymers and their compounds.
- Q: What is the primary role of the Production team in the EVA chemical and compounding section?
- A: The primary role of the Production team is to execute the manufacturing processes, operate machinery, ensure efficient production, and maintain safety and quality standards during the actual production of EVA and its compounds.
- Q: How do Chemists and the Production team collaborate?
- A: They collaborate closely through communication, sharing data, troubleshooting issues, and implementing process improvements. Chemists provide technical expertise, while Production provides practical feedback.
- Q: What is EVA?
- A: EVA stands for Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate, a copolymer widely used for its elasticity, flexibility, toughness, and good clarity.
- Q: What is “compounding” in the context of EVA?
- A: Compounding involves mixing EVA resin with various additives (e.g., colorants, stabilizers, fillers, flame retardants) to achieve specific properties for different applications.
Chemist’s Role: Research & Development (R&D)
- Q: How do Chemists contribute to new EVA product development?
- A: Chemists develop new EVA formulations, research novel additives, optimize material properties, and scale up laboratory processes for production.
- Q: What is the significance of “formulation” for a Chemist?
- A: Formulation is crucial as it dictates the final properties of the EVA compound. Chemists carefully select and proportion ingredients to meet desired specifications.
- Q: How do Chemists evaluate new raw materials?
- A: They perform laboratory tests to assess purity, compatibility, and performance of new raw materials before approving them for production.
- Q: What is pilot plant scale-up in R&D?
- A: It’s the process where Chemists take a successful lab-scale formulation and adapt it for larger-scale production in a pilot plant, identifying and resolving any scale-up challenges.
- Q: How do Chemists address customer specific requirements for EVA?
- A: They work to understand customer needs, then develop or modify existing EVA formulations to meet those unique performance criteria.
Chemist’s Role: Quality Control (QC) & Assurance (QA)
- Q: What is the Chemist’s role in Quality Control (QC)?
- A: Chemists establish QC parameters, develop testing methodologies, analyze samples from production, and ensure that the final product meets specified quality standards.
- Q: How do Chemists ensure raw material quality?
- A: They set specifications for incoming raw materials and conduct tests (e.g., FTIR, DSC, MFI) to verify that materials meet these standards before use.
- Q: What types of tests do Chemists perform on EVA compounds?
- A: They perform tests like Melt Flow Index (MFI), density, hardness (Shore A/D), tensile strength, elongation at break, Vicat softening point, and FTIR analysis.
- Q: What happens if a batch fails QC?
- A: The Chemist investigates the cause of the failure, identifies deviations, and works with the Production team to implement corrective actions or rework the batch if possible.
- Q: How do Chemists contribute to Quality Assurance (QA)?
- A: They help develop and implement QA systems, standard operating procedures (SOPs), and documentation to ensure consistent product quality over time.
Chemist’s Role: Technical Support & Troubleshooting
- Q: How do Chemists support the Production team during manufacturing?
- **A: They provide technical guidance, help troubleshoot processing issues (e.g., inconsistent melt flow, poor mixing), and offer solutions to optimize production.
- Q: What kind of processing issues might a Chemist troubleshoot?
- A: Issues like gels, discoloration, inconsistent extrusion, poor dispersion of additives, or material degradation during processing.
- Q: How do Chemists respond to customer complaints regarding product performance?
- A: They analyze returned samples, investigate the root cause of the issue, and recommend solutions or product adjustments to resolve the complaint.
- Q: Do Chemists train Production personnel?
- A: Yes, they often provide training on new formulations, testing procedures, and best practices for handling and processing chemical ingredients.
- Q: How do Chemists contribute to process optimization?
- A: They analyze production data, suggest adjustments to processing parameters (e.g., temperature profiles, screw speed) to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance product quality.
Production Team’s Role: Operations & Manufacturing
- Q: What is the core responsibility of the Production team?
- A: To efficiently and safely manufacture EVA compounds according to established procedures and quality specifications.
- Q: What types of equipment does the Production team operate in EVA compounding?
- A: They operate mixers (e.g., Banbury, internal mixers), extruders (single or twin screw), pelletizers, cooling systems, and packaging equipment.
- Q: How does the Production team ensure safety in the plant?
- A: By strictly following safety protocols, using proper PPE, conducting regular equipment checks, and participating in safety training.
- Q: What is the role of Production in maintaining equipment?
- A: They perform routine checks, basic maintenance, and report any malfunctions to maintenance personnel to ensure continuous operation.
- Q: How does the Production team handle raw materials?
- A: They ensure proper storage, accurate weighing, and correct feeding of raw materials into the compounding equipment according to the batch sheet.
Production Team’s Role: Process Execution & Monitoring
- Q: How does the Production team ensure proper mixing of ingredients?
- A: They monitor mixer parameters like temperature, torque, and time, ensuring all components are uniformly blended according to the recipe.
- Q: What are “batch sheets” and how does the Production team use them?
- A: Batch sheets are detailed instructions for manufacturing a specific product. The Production team follows them precisely to ensure correct material quantities and processing steps.
- Q: How does the Production team monitor product quality during a run?
- A: They perform in-process checks (e.g., visual inspection, touch tests, basic MFI checks) and collect samples for the QC lab.
- Q: What is the importance of process parameters (e.g., temperature, pressure, speed)?
- A: These parameters are critical for achieving the desired product properties. The Production team must maintain them within specified ranges.
- Q: How does the Production team handle finished products?
- A: They ensure proper cooling, pelletizing, packaging, labeling, and storage of the finished EVA compounds.
Production Team’s Role: Troubleshooting & Efficiency
- Q: What immediate actions does the Production team take when an issue arises?
- A: They identify the problem (e.g., alarm, unusual noise, off-spec material), attempt initial troubleshooting based on training, and report critical issues to the supervisor and/or Chemist.
- Q: How does the Production team contribute to waste reduction?
- A: By optimizing material usage, minimizing spills, properly segregating waste, and ensuring efficient equipment operation to reduce off-spec material.
- Q: How does the Production team ensure efficient changeovers between products?
- A: By following systematic cleaning procedures, preparing equipment, and having necessary materials readily available.
- Q: What is the role of continuous improvement for the Production team?
- A: They provide feedback on process bottlenecks, suggest minor adjustments, and participate in initiatives aimed at increasing efficiency and quality.
- Q: How does the Production team contribute to cost control?
- A: By minimizing downtime, reducing material scrap, optimizing energy consumption, and operating equipment efficiently.
Interdepartmental Interactions & Overlaps
- Q: Who initiates a new product run in the plant?
- A: Typically, the Production Planning department, based on sales orders and forecasts, with formulations provided by the R&D/QC Chemists.
- Q: How is feedback from Production used by Chemists?
- A: Production feedback on material handling, processing ease, and common issues helps Chemists refine formulations and improve process robustness.
- Q: In case of a major deviation, who takes the lead in resolving it?
- A: A collaborative effort, but the Chemist often takes the lead in determining the root chemical/material cause, while Production executes corrective actions on the floor.
- Q: How do new regulatory requirements impact both teams?
- A: Chemists adapt formulations to comply, while the Production team implements new procedures and ensures safe handling and disposal in line with regulations.
- Q: What is the role of documentation for both teams?
- A: Both teams maintain meticulous records. Chemists document formulations and test results, while Production records batch data, process parameters, and production output.
Career & Skills
- Q: What educational background is typically required for a Chemist?
- A: A Bachelor’s, Master’s, or Ph.D. in Chemistry, Polymer Science, Chemical Engineering, or a related scientific field.
- Q: What skills are essential for an EVA Chemist?
- A: Analytical thinking, problem-solving, attention to detail, knowledge of polymer chemistry, laboratory skills, and data interpretation.
- Q: What educational background is typically required for the Production team?
- A: Often a high school diploma, vocational training, or an associate’s degree in a relevant technical field. On-the-job training is also significant.
- Q: What skills are essential for an EVA Production team member?
- A: Mechanical aptitude, adherence to procedures, physical stamina, attention to safety, teamwork, and problem-solving at the operational level.
- Q: Can a Production team member become a Chemist?
- A: While less common without formal education, a highly experienced Production team member might transition into a technical support or junior lab role with further training and education.
- Q: Can a Chemist work in Production?
- A: Chemists often spend time on the production floor for troubleshooting, new product trials, and process optimization, gaining valuable practical experience.
- Q: What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) for Chemists?
- A: Successful new product launches, reduced quality non-conformances, accuracy of analytical results, and efficiency of problem resolution.
- Q: What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) for the Production team?
- A: Production output, on-time delivery, yield, waste reduction, safety record, and equipment utilization.
- Q: How does automation impact these roles?
- A: Automation can streamline data collection (for Chemists) and simplify some operational tasks (for Production), but it increases the need for analytical and troubleshooting skills in both roles.
- Q: What is the ultimate shared goal of both teams?
- A: To consistently produce high-quality, cost-effective EVA compounds that meet customer specifications and contribute to the company’s success.
Role of Human Resources in EVA Chemical and Compounding Section
General Role & Strategic Alignment
- Q: What is the primary role of HR in an EVA Chemical and Compounding section?
- A: The primary role is to align HR strategies with the business objectives of the EVA chemical and compounding section, ensuring a skilled, motivated, and compliant workforce that drives productivity and innovation.
- Q: How does HR contribute to the overall success of the EVA section?
- A: HR contributes by attracting and retaining top talent, fostering a positive work environment, developing employee skills, ensuring safety and compliance, and optimizing human capital to achieve production and quality targets.
- Q: What specific challenges does HR face in the EVA chemical industry?
- A: Challenges include managing a specialized workforce, ensuring strict safety protocols, navigating chemical handling regulations, addressing potential health hazards, and adapting to technological advancements in compounding.
- Q: How does HR ensure compliance with chemical industry regulations (e.g., REACH, GHS)?
- A: HR collaborates with EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety) to implement training programs on regulations, ensures proper documentation for employee exposure, and updates policies to reflect legal requirements.
- Q: How does HR support innovation within the EVA compounding section?
- A: HR supports innovation by fostering a culture of continuous learning, facilitating cross-functional collaboration, implementing reward systems for new ideas, and recruiting individuals with strong R&D capabilities.
- Q: What is HR’s role in the EVA section’s digital transformation initiatives?
- A: HR plays a crucial role in managing the human aspect of digital transformation, including identifying new skill requirements, facilitating training on new technologies, and managing change to ensure smooth adoption.
Talent Acquisition & Recruitment
- Q: What specific skills does HR look for when recruiting for an EVA compounding section?
- A: HR seeks candidates with backgrounds in chemistry, chemical engineering, material science, process operation, quality control, and a strong understanding of safety procedures in chemical environments.
- Q: How does HR attract specialized talent to the EVA chemical industry?
- A: HR utilizes targeted recruitment strategies, industry partnerships, university collaborations, competitive compensation packages, and highlights career growth opportunities within the specialized field.
- Q: What is the onboarding process like for new hires in the EVA section?
- A: Onboarding is comprehensive, including safety training, site-specific hazard communication, equipment operation procedures, quality control protocols, and mentorship to ensure a smooth integration.
- Q: How does HR ensure diversity and inclusion in its recruitment efforts for the EVA section?
- A: HR implements inclusive recruitment practices, partners with diverse professional organizations, and promotes an equitable work environment to attract a wide range of candidates.
- Q: What role does HR play in assessing technical competencies during recruitment?
- A: HR collaborates with technical managers to design skill assessments, interviews, and practical tests to accurately evaluate a candidate’s technical proficiency and experience.
Training & Development
- Q: What types of training are essential for employees in an EVA chemical and compounding section?
- A: Essential training includes safety protocols (HAZOP, LOTO), chemical handling, quality control, process optimization, equipment operation, emergency response, and regulatory compliance.
- Q: How does HR identify training needs for different roles within the EVA section?
- A: HR conducts needs assessments through performance reviews, skills gap analyses, departmental feedback, and stays updated on industry trends and technological advancements.
- Q: How does HR ensure that safety training is effective and regularly updated?
- A: HR collaborates with EHS to deliver engaging safety training, conducts drills, incorporates real-world scenarios, and ensures annual refreshers based on incident reports and regulatory changes.
- Q: Does HR facilitate cross-training within the EVA compounding section?
- A: Yes, HR encourages and facilitates cross-training to enhance flexibility, improve problem-solving, and provide career development opportunities for employees.
- Q: How does HR support leadership development for supervisors and managers in the EVA section?
- A: HR offers leadership programs, coaching, mentorship opportunities, and management training specific to the challenges and responsibilities of leading teams in a chemical manufacturing environment.
Performance Management & Compensation
- Q: How does HR design performance metrics for roles in the EVA compounding section?
- A: HR works with operational managers to define measurable KPIs such as production output, quality adherence, safety compliance, efficiency, and waste reduction.
- Q: What is HR’s role in performance reviews and feedback processes for the EVA section?
- A: HR provides guidance on performance review cycles, trains managers on effective feedback delivery, and ensures fairness and consistency in evaluations.
- Q: How does HR handle underperformance in a critical environment like EVA compounding?
- A: HR implements a clear performance improvement plan (PIP) process, provides necessary support and training, and takes appropriate disciplinary action when improvement is not met.
- Q: What compensation strategies does HR employ to attract and retain talent in the EVA chemical industry?
- A: HR conducts market benchmarking, offers competitive base salaries, performance-based bonuses, benefits packages (health, retirement), and considers industry-specific allowances.
- Q: How does HR ensure equitable compensation across different roles and experience levels?
- A: HR uses job evaluations, salary bands, and market data to ensure internal equity and external competitiveness, promoting fair pay practices.
Employee Relations & Welfare
- Q: How does HR foster a positive and collaborative work environment in the EVA section?
- A: HR promotes open communication, team-building activities, recognition programs, and addresses conflicts promptly and constructively.
- Q: What is HR’s approach to resolving conflicts or grievances within the EVA compounding section?
- A: HR follows a structured grievance procedure, mediating disputes, conducting investigations, and ensuring fair and impartial resolutions.
- Q: How does HR support employee well-being and mental health in a demanding chemical environment?
- A: HR offers employee assistance programs (EAP), promotes work-life balance initiatives, and provides resources for stress management and mental health support.
- Q: What measures does HR take to ensure a safe and healthy workplace beyond basic compliance?
- A: HR collaborates with EHS on proactive safety campaigns, promotes a strong safety culture, encourages incident reporting, and implements wellness programs.
- Q: How does HR manage shift work and its impact on employee welfare in a 24/7 operation?
- A: HR develops fair shift schedules, ensures compliance with labor laws regarding breaks and rest periods, and provides resources for managing fatigue.
Safety & Compliance
- Q: What is HR’s specific responsibility regarding safety in the EVA chemical environment?
- A: HR ensures all employees receive mandatory safety training, understand emergency procedures, and are aware of their responsibilities in maintaining a safe workplace.
- Q: How does HR collaborate with the EHS department in the EVA section?
- A: HR and EHS collaborate closely on safety training, incident investigation, compliance audits, development of safety policies, and promotion of a safety-first culture.
- Q: What is HR’s role in incident investigation and reporting in the EVA section?
- A: HR participates in incident investigations, ensures proper documentation, advises on disciplinary actions if safety protocols were violated, and supports return-to-work programs.
- Q: How does HR handle regulatory audits related to human resources in the chemical industry?
- A: HR prepares necessary documentation (training records, certifications), ensures compliance with labor laws and industry-specific regulations, and cooperates with auditors.
- Q: What steps does HR take to ensure all employees are aware of and adhere to safety data sheets (SDS)?
- A: HR ensures SDS are readily accessible, integrates SDS information into training programs, and verifies employees understand the hazards and safe handling procedures for all chemicals.
Succession Planning & Retention
- Q: How does HR approach succession planning for critical roles in the EVA compounding section?
- A: HR identifies high-potential employees, provides development opportunities, and creates clear career paths to ensure a pipeline of qualified successors for key positions.
- Q: What strategies does HR use to retain experienced talent in the EVA chemical industry?
- A: HR implements retention strategies such as competitive compensation, professional development, challenging assignments, recognition programs, and a positive work environment.
- Q: How does HR manage knowledge transfer from retiring or departing employees in the EVA section?
- A: HR facilitates knowledge transfer through mentorship programs, documentation of critical processes, and ensuring new hires shadow experienced personnel.
- Q: What role does HR play in career development for employees in the EVA compounding section?
- A: HR provides career counseling, identifies training and development opportunities, and helps employees align their career aspirations with organizational needs.
Legal & Ethical Considerations
- Q: How does HR ensure compliance with labor laws specific to the chemical manufacturing industry?
- A: HR stays updated on all relevant labor laws, including those related to working hours, hazardous materials, and environmental protection, implementing policies accordingly.
- Q: What is HR’s role in preventing discrimination and harassment in the EVA section?
- A: HR implements clear anti-discrimination and anti-harassment policies, provides mandatory training, and has a robust process for investigating and addressing complaints.
- Q: How does HR handle confidential employee information in a sensitive industry like chemicals?
- A: HR adheres to strict data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR), implements secure data storage, and restricts access to confidential employee information.
- Q: What ethical considerations does HR prioritize in its operations within the EVA compounding section?
- A: HR prioritizes fairness, transparency, integrity, respect for employees, and upholding the company’s ethical standards in all decisions and interactions.
- Q: How does HR manage disciplinary actions in the EVA section, particularly concerning safety violations?
- A: HR ensures disciplinary actions are fair, consistent, and adhere to company policy and labor laws, especially when safety protocols are breached, to reinforce accountability.
Future Trends & Technology
- Q: How is HR leveraging technology (e.g., HRIS, AI) in the EVA compounding section?
- A: HR uses HRIS for streamlined administration, explores AI for recruitment analytics, and leverages digital platforms for training delivery and employee communication.
- Q: What impact do automation and robotics have on HR’s role in the EVA section?
- A: Automation necessitates HR to focus on upskilling the workforce for new roles, managing workforce transitions, and ensuring the human-robot interface is safe and efficient.
- Q: How does HR prepare the workforce for future skills needed in the evolving EVA chemical industry?
- A: HR conducts future skills assessments, invests in reskilling and upskilling programs, and fosters a culture of continuous learning and adaptability.
- Q: What is HR’s role in attracting and retaining Gen Z talent in the EVA compounding section?
- A: HR understands Gen Z’s values (purpose, technology, work-life balance) and tailors recruitment, development, and work environment strategies to appeal to them.
- Q: How does HR support remote or hybrid work models, if applicable, in the EVA chemical industry?
- A: For roles that can be remote, HR develops policies for remote work, ensures necessary technology, and maintains engagement and productivity of remote employees. (Note: This is less common for hands-on compounding roles).
Specialized & Niche Topics
- Q: How does HR manage potential exposure to chemicals and ensure employee health monitoring?
- A: HR works with occupational health professionals to implement health monitoring programs, educate employees on exposure risks, and ensure proper PPE usage.
- Q: What is HR’s role in managing union relations (if applicable) in the EVA chemical section?
- A: HR plays a crucial role in collective bargaining, interpreting union agreements, resolving grievances, and maintaining positive labor-management relations.
- Q: How does HR support environmental sustainability initiatives within the EVA section?
- A: HR promotes employee awareness and participation in sustainability efforts, encourages green practices, and aligns HR policies with the company’s environmental goals.
- Q: What is HR’s involvement in crisis management and emergency response for the EVA section?
- A: HR assists in communication during crises, supports employee well-being, manages post-crisis support, and ensures employee awareness of emergency procedures.
- Q: How does HR measure its effectiveness and contribution to the EVA compounding section’s bottom line?
- A: HR measures effectiveness through metrics such as turnover rates, time-to-hire, training ROI, safety incident rates, employee engagement scores, and productivity improvements.
Role of Production Supervisor in EVA Chemical and Compounding Section
General Role & Responsibilities
- Q: What is the primary role of a Production Supervisor in the EVA Chemical and Compounding section?
- A: To oversee and manage all aspects of the production process, ensuring efficiency, safety, quality, and adherence to production schedules and targets.
- Q: What is EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate)?
- A: EVA is a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate, widely used in applications requiring flexibility, clarity, and good impact resistance, often found in foams, films, adhesives, and more.
- Q: What does the “Chemical” part of the section refer to?
- A: This typically refers to the polymerization process where ethylene and vinyl acetate monomers are reacted to form the EVA polymer.
- Q: What does the “Compounding” part of the section refer to?
- A: Compounding involves blending the base EVA polymer with various additives (e.g., colorants, stabilizers, fillers) to achieve specific properties for different end-use applications.
- Q: What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) a Production Supervisor is typically responsible for?
- A: Production output, yield, quality metrics (e.g., melt index, density), safety incident rates, downtime, and cost efficiency.
- Q: How does a Production Supervisor contribute to overall company goals?
- A: By optimizing production processes, reducing waste, ensuring product quality, and maintaining a safe work environment, directly contributing to profitability and customer satisfaction.
Operational Management
- Q: How does a Production Supervisor ensure production targets are met?
- A: By planning and scheduling production runs, allocating resources effectively, monitoring progress, and addressing any deviations or bottlenecks.
- Q: What is the supervisor’s role in managing raw materials?
- A: Ensuring availability of raw materials, coordinating with inventory and procurement, minimizing waste, and verifying quality upon receipt.
- Q: How do they manage finished product inventory?
- A: Overseeing the movement of finished goods to storage, ensuring proper labeling, and coordinating with logistics for shipment.
- Q: What is involved in scheduling production shifts?
- A: Creating fair and efficient shift rotations, ensuring adequate staffing levels, and managing leave requests.
- Q: How does a supervisor optimize machine utilization?
- A: By minimizing idle time, ensuring proper machine setup, coordinating maintenance activities, and optimizing operating parameters.
- Q: What is the role in process optimization?
- A: Continuously looking for ways to improve efficiency, reduce cycle times, minimize energy consumption, and enhance product quality through process adjustments.
- Q: How do they handle production bottlenecks?
- A: Identifying the root cause of the bottleneck, reallocating resources, adjusting schedules, or collaborating with engineering for solutions.
- Q: What is their involvement in new product introductions (NPI)?
- A: Assisting with trials, setting up new production lines or processes, and training staff on new product specifications and procedures.
- Q: How do they ensure equipment is running smoothly?
- A: Regular checks, coordinating with maintenance for preventive and corrective actions, and ensuring operators are trained on basic equipment care.
Quality Control & Assurance
- Q: How does a Production Supervisor ensure product quality?
- A: By enforcing standard operating procedures (SOPs), conducting in-process checks, reviewing quality control data, and initiating corrective actions for non-conformances.
- Q: What is their role in quality deviations or non-conformances?
- A: Investigating the root cause, isolating affected products, implementing corrective and preventive actions, and documenting all findings.
- Q: How do they interact with the Quality Control (QC) department?
- A: Collaborating on quality issues, understanding QC reports, and ensuring production adheres to QC standards and specifications.
- Q: What is batch traceability and why is it important?
- A: Tracking all raw materials, process parameters, and finished product information for each batch. It’s crucial for troubleshooting, recalls, and continuous improvement.
- Q: How do they contribute to continuous quality improvement?
- **A: By analyzing production data, identifying trends in defects or inefficiencies, and proposing solutions to improve product quality over time.
Safety, Health, and Environment (HSE)
- Q: What is the Production Supervisor’s primary responsibility regarding safety?
- A: Ensuring a safe working environment for all personnel, preventing accidents, and promoting a strong safety culture.
- Q: How do they implement safety protocols?
- A: Enforcing personal protective equipment (PPE) usage, conducting regular safety audits, ensuring compliance with lockout/tagout procedures, and training staff on safe work practices.
- Q: What is their role in incident investigation?
- A: Leading or assisting in investigations of accidents or near misses, identifying root causes, and implementing corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
- Q: How do they ensure environmental compliance?
- A: Ensuring proper handling and disposal of chemicals, monitoring emissions, and adhering to all environmental regulations.
- Q: What is their role in emergency preparedness?
- A: Training staff on emergency procedures (e.g., fire drills, chemical spills), ensuring emergency equipment is accessible and functional.
- Q: How do they promote a safety-conscious culture?
- A: Leading by example, encouraging open communication about safety concerns, recognizing safe behaviors, and providing regular safety reminders.
Team Leadership & Development
- Q: How does a Production Supervisor lead their team?
- A: By setting clear expectations, providing guidance, motivating staff, fostering teamwork, and recognizing achievements.
- Q: What is their role in staff training and development?
- A: Identifying training needs, providing on-the-job training, coaching, and facilitating access to external training programs to enhance skills.
- Q: How do they manage performance of their team members?
- **A: Setting performance goals, providing regular feedback, conducting performance reviews, and addressing performance issues constructively.
- Q: How do they handle conflicts within the team?
- **A: Mediating disputes, encouraging respectful communication, and finding solutions that promote a harmonious work environment.
- Q: What is their role in employee engagement?
- **A: Creating a positive work environment, involving employees in decision-making where appropriate, and listening to their feedback and suggestions.
- Q: How do they delegate tasks effectively?
- **A: Assigning tasks based on individual strengths and development needs, providing clear instructions, and empowering team members.
- Q: How do they foster a culture of continuous improvement within the team?
- **A: Encouraging employees to identify problems, propose solutions, and embrace changes that lead to better efficiency and quality.
Documentation & Reporting
- Q: What kind of reports does a Production Supervisor typically generate?
- A: Daily production reports, shift handover reports, quality deviation reports, incident reports, and downtime analyses.
- Q: Why is accurate record-keeping important?
- A: For traceability, compliance, performance analysis, troubleshooting, and continuous improvement initiatives.
- Q: How do they use data for decision-making?
- **A: Analyzing production data, efficiency metrics, and quality reports to identify trends, pinpoint areas for improvement, and make informed operational decisions.
- Q: What is the importance of clear communication in documentation?
- **A: To ensure all stakeholders understand the information, prevent misunderstandings, and facilitate smooth operations across shifts and departments.
- Q: How do they ensure compliance with regulatory documentation requirements?
- **A: Staying updated on relevant regulations, ensuring all required documents are completed accurately, and maintaining organized records.
Interdepartmental Collaboration
- Q: How does a Production Supervisor interact with the Maintenance department?
- **A: Coordinating planned maintenance, reporting equipment breakdowns, and prioritizing repairs to minimize production downtime.
- Q: What is their relationship with the Engineering department?
- **A: Collaborating on process improvements, new equipment installations, and resolving complex technical issues.
- Q: How do they work with the Logistics/Warehouse department?
- **A: Coordinating raw material deliveries, finished goods transfers, and ensuring efficient flow of materials.
- Q: What is their interaction with the Research & Development (R&D) department?
- **A: Assisting with pilot plant trials, providing feedback on new formulations, and ensuring scalability of new products.
- Q: How do they collaborate with the Sales and Marketing teams?
- **A: Understanding customer requirements, communicating production capabilities, and assisting in meeting specific customer orders.
- Q: Why is effective cross-functional communication crucial?
- **A: To ensure alignment of goals, resolve issues quickly, prevent misunderstandings, and optimize overall operational efficiency.
Problem Solving & Decision Making
- Q: How does a Production Supervisor approach problem-solving?
- **A: Using systematic approaches like root cause analysis, gathering data, collaborating with the team, and implementing sustainable solutions.
- Q: What kind of decisions do they make daily?
- **A: Operational decisions regarding production schedules, resource allocation, quality adjustments, and immediate responses to equipment issues.
- Q: How do they prioritize tasks and issues?
- **A: Based on impact on safety, quality, production targets, and cost, using frameworks like urgency-importance matrix.
- Q: What is the role of critical thinking in their job?
- **A: Essential for analyzing complex situations, anticipating potential problems, and making sound judgments under pressure.
- Q: How do they handle unexpected breakdowns or emergencies?
- **A: Remaining calm, assessing the situation, implementing emergency procedures, coordinating with relevant departments, and communicating impacts.
- Q: What makes a successful Production Supervisor in the EVA Chemical and Compounding section?
- **A: A combination of strong technical knowledge, leadership skills, problem-solving abilities, excellent communication, and a commitment to safety and quality.
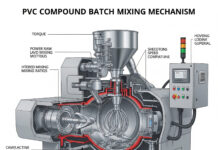
EVA Chemical and Compounding in Kneader Machines
Section 1: General EVA & Kneader Basics
- Q: What is EVA?
- A: EVA is an acronym for Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate, a thermoplastic copolymer made from ethylene and vinyl acetate monomers. It’s known for its flexibility, elasticity, and good impact strength.
- Q: Why is EVA commonly processed in kneader machines?
- A: Kneader machines (like internal mixers or Banbury mixers) are ideal for EVA compounding due to their high shear mixing capabilities, which are essential for dispersing fillers, pigments, and other additives uniformly into the viscous EVA matrix.
- Q: What are the primary applications of EVA compounds made in kneaders?
- A: Common applications include foam (e.g., shoe soles, mats), wire and cable insulation, hot-melt adhesives, solar encapsulation films, flexible packaging, and various molded articles.
- Q: What is the typical temperature range for EVA compounding in a kneader?
- A: The temperature range usually falls between 90°C and 160°C, depending on the EVA grade, additives, and desired viscosity. Lower temperatures are used for initial mixing, higher for final dispersion.
- Q: What is the typical fill factor for a kneader when compounding EVA?
- A: A typical fill factor for EVA compounding is usually between 65% and 80% of the mixing chamber volume. This ensures optimal shear and material turnover.
Section 2: EVA Grades & Properties
- Q: How does Vinyl Acetate (VA) content affect EVA properties?
- A: Higher VA content generally increases flexibility, elasticity, softness, adhesion, and melt flow index (MFI), while decreasing crystallinity, hardness, and melting point.
- Q: What is the significance of Melt Flow Index (MFI) for EVA in kneaders?
- A: MFI indicates the melt viscosity. Higher MFI means lower viscosity, which can be easier to process but may require more careful temperature control to prevent degradation. Lower MFI indicates higher viscosity, requiring more energy to mix.
- Q: Are there different grades of EVA for different applications?
- A: Yes, EVA grades vary significantly in VA content (from 5% to 50% or more), MFI, and molecular weight, each tailored for specific end-use properties and processing methods.
- Q: How does molecular weight influence EVA processing in a kneader?
- A: Higher molecular weight EVA generally has higher melt viscosity and strength, requiring more energy and potentially longer mixing times in the kneader to achieve proper dispersion.
- Q: Can different EVA grades be blended in a kneader?
- A: Yes, blending different EVA grades is common to achieve desired property combinations, such as balancing flexibility with hardness or adjusting processing characteristics.
Section 3: Additives & Their Functions
- Q: What are the most common additives used with EVA in a kneader?
- A: Common additives include fillers (calcium carbonate, talc), pigments, blowing agents, crosslinking agents (peroxides), antioxidants, UV stabilizers, processing aids, and flame retardants.
- Q: Why are fillers used in EVA compounding?
- A: Fillers are used to reduce cost, increase stiffness, improve dimensional stability, enhance heat resistance, and sometimes improve certain mechanical properties.
- Q: What are the challenges of incorporating high filler loadings into EVA in a kneader?
- A: Challenges include achieving good dispersion, maintaining mechanical properties, managing increased viscosity, and preventing excessive heat build-up.
- Q: What role do processing aids play in EVA compounding?
- A: Processing aids (e.g., stearates, waxes) reduce melt viscosity, improve flow, enhance dispersion of fillers, prevent sticking to the mixer walls, and reduce power consumption.
- Q: When are crosslinking agents added to EVA in a kneader?
- A: Crosslinking agents (like peroxides) are added when the EVA compound is intended for applications requiring improved heat resistance, tensile strength, and reduced creep (e.g., foams, wire insulation). They are typically added in the final stages of mixing to avoid premature crosslinking.
- Q: How do blowing agents work in EVA foam compounding?
- A: Blowing agents (e.g., azodicarbonamide) decompose at elevated temperatures to release gas (nitrogen, carbon dioxide), which creates a cellular structure in the EVA matrix during the molding or extrusion process.
- Q: Why are antioxidants crucial in EVA compounding?
- A: Antioxidants prevent oxidative degradation of EVA during processing at high temperatures and during its service life, preserving its mechanical and aesthetic properties.
- Q: What are UV stabilizers used for in EVA compounds?
- A: UV stabilizers protect EVA from degradation caused by ultraviolet radiation, which can lead to discoloration, embrittlement, and loss of mechanical properties, especially in outdoor applications.
- Q: How are pigments incorporated into EVA in a kneader?
- A: Pigments, often in masterbatch form or as powders, are added early in the mixing cycle to allow for sufficient shear and time for uniform dispersion throughout the EVA matrix.
- Q: What types of flame retardants are compatible with EVA?
- A: Common flame retardants include halogenated compounds, phosphorus-based compounds, and inorganic hydroxides (e.g., magnesium hydroxide, aluminum trihydrate), selected based on desired performance and regulatory requirements.
Section 4: Kneader Machine Operation & Parameters
- Q: What are the key operational parameters for a kneader when compounding EVA?
- A: Key parameters include rotor speed, mixing temperature, mixing time, fill factor, and ram pressure.
- Q: How does rotor speed affect EVA compounding?
- A: Higher rotor speed increases shear and heat generation, leading to faster mixing and better dispersion but also a risk of degradation if not controlled. Lower speeds provide gentler mixing.
- Q: What is the optimal mixing temperature profile for EVA in a kneader?
- A: A common approach is a staged temperature profile: lower temperatures initially for pre-blending and incorporating heat-sensitive additives, followed by higher temperatures for final dispersion and melting.
- Q: How is mixing time determined for EVA compounds?
- A: Mixing time is determined by the desired level of dispersion, the specific EVA grade, the types and amounts of additives, and the kneader’s efficiency. It’s often optimized through trials.
- Q: What is the purpose of the ram in a kneader during EVA compounding?
- A: The ram applies pressure to the material, forcing it into the mixing rotors, ensuring consistent shear, and preventing material from escaping the mixing chamber prematurely.
- Q: How can excessive heat build-up be controlled during EVA compounding?
- A: Heat build-up can be controlled by optimizing rotor speed, using cooling systems (water jackets on the mixing chamber), adding processing aids, and adjusting the fill factor.
- Q: What are the signs of poor dispersion in an EVA compound from a kneader?
- A: Signs include streaks, gels, unmixed agglomerates of fillers or pigments, inconsistent color, and reduced mechanical properties.
- Q: How do you know when the EVA compound is adequately mixed?
- A: Adequate mixing is indicated by a uniform appearance, consistent color, a stable temperature curve, and the achievement of target torque or power consumption values.
- Q: What is the typical sequence of adding ingredients to a kneader for EVA compounding?
- A: Typically, EVA resin is added first, followed by major fillers, then pigments, and finally heat-sensitive additives like antioxidants, processing aids, and crosslinking agents.
- Q: What are the safety considerations when operating a kneader with EVA chemicals?
- A: Safety considerations include proper ventilation for fumes, personal protective equipment (PPE), lockout/tagout procedures for maintenance, and adherence to material safety data sheets (MSDS) for all chemicals.
Section 5: Quality Control & Troubleshooting
- Q: What quality control tests are performed on EVA compounds?
- A: Common tests include MFI, hardness (Shore A/D), tensile strength, elongation at break, density, color matching, and specific tests for individual applications (e.g., heat aging, compression set for foam).
- Q: How do you troubleshoot poor dispersion in an EVA compound?
- A: Troubleshoot by increasing mixing time, increasing rotor speed, adjusting processing aids, reducing filler loading, or ensuring proper feed sequence.
- Q: What causes scorching or premature crosslinking in EVA during kneading?
- A: Scorching is caused by excessive temperature (too high rotor speed, insufficient cooling) or incorrect addition sequence/concentration of crosslinking agents.
- Q: How can material sticking to the kneader rotors or walls be prevented?
- A: Use processing aids, optimize temperature, ensure proper fill factor, and maintain clean internal surfaces of the kneader.
- Q: What are the common causes of inconsistent batch quality in EVA compounding?
- A: Inconsistent raw material quality, variations in feeding accuracy, inconsistent mixing parameters (time, temperature, speed), and human error.
- Q: How to handle EVA degradation during kneading?
- A: Prevent degradation by optimizing processing temperatures, minimizing residence time, using appropriate antioxidants, and avoiding excessive shear.
- Q: What is the importance of cooling the compound after kneading?
- A: Cooling the compound (e.g., on a two-roll mill or pelietizer) is essential to prevent further thermal degradation, allow for easier handling, and ensure product stability before subsequent processing.
- Q: Can recycled EVA be used in a kneader?
- A: Yes, recycled EVA can be processed in a kneader, but its properties may be degraded, and adjustments to formulation (e.g., adding fresh resin, stabilizers) might be needed to maintain quality.
- Q: How often should the kneader be cleaned when processing EVA?
- A: Cleaning frequency depends on the materials being processed (e.g., color changes require thorough cleaning) and the level of contamination. Regular cleaning prevents cross-contamination and maintains product quality.
- Q: What information should be recorded for each EVA batch processed in a kneader?
- A: Batch number, date, time, raw material lot numbers, mixing parameters (temperature profile, rotor speed, time), power consumption, operator, and any observations or issues.
Section 6: Advanced Topics & Optimizations
- Q: What is the role of rheology in optimizing EVA compounding in a kneader?
- A: Rheological analysis helps understand the flow behavior of EVA and its compounds, allowing for optimization of processing parameters, prediction of processability, and design of appropriate formulations.
- Q: How can energy consumption be minimized during EVA kneading?
- A: Optimize processing aids, ensure proper fill factor, maintain the kneader in good condition, and optimize rotor speed for efficient mixing without excessive shear.
- Q: What are the benefits of using a two-stage mixing process for EVA?
- A: A two-stage process (e.g., initial mixing in a kneader, then a second pass or transfer to an extruder) allows for better control of heat-sensitive additives, improved dispersion, and reduced overall cycle time for complex formulations.
- Q: How does the type of rotor (intermeshing vs. tangential) affect EVA compounding?
- A: Tangential rotors provide high shear at the nip, suitable for breaking down agglomerates and dispersing fillers. Intermeshing rotors offer more uniform shear throughout the chamber, good for homogenization and incorporating soft additives. The choice depends on the specific compound and desired outcome.
- Q: What are the challenges of compounding highly filled EVA for specific applications (e.g., solar encapsulation)?
- A: Challenges include achieving high filler loading without compromising transparency or mechanical properties, ensuring excellent dispersion, and maintaining UV stability and adhesion.
- Q: How can you optimize the cooling system of a kneader for EVA?
- A: Ensure adequate water flow, proper temperature of cooling water, and clean cooling channels to maximize heat removal efficiency.
- Q: What is the impact of moisture on EVA compounding?
- A: Moisture can cause bubbling, porosity, and reduced mechanical properties in the final product. It’s crucial to ensure raw materials are dry, especially fillers.
- Q: Can a kneader be used for reactive compounding of EVA?
- A: Yes, kneaders can be used for reactive compounding, where chemical reactions (e.g., grafting, crosslinking) occur during the mixing process, but this requires careful control of temperature and reaction kinetics.
- Q: What advancements are being made in kneader technology for EVA compounding?
- A: Advancements include improved rotor designs for better dispersion and energy efficiency, enhanced temperature control systems, automation for consistent feeding and monitoring, and integration with downstream equipment.
- Q: Where can I find more detailed information or support for EVA compounding in kneaders?
- A: Consult material suppliers’ technical data sheets, kneader machine manufacturers’ manuals, specialized polymer compounding textbooks, and industry associations.
Role of Conveyor Machines in EVA Chemical and Compounding Section
General & Introduction
- Q: What is the primary function of conveyor machines in an EVA chemical and compounding section? A: Their primary function is to efficiently and continuously transport raw materials, intermediate products, and finished compounds throughout various stages of the manufacturing process, minimizing manual handling and optimizing workflow.
- Q: Why are conveyor machines crucial for EVA compounding? A: They ensure consistent material flow, reduce labor costs, improve safety, maintain product quality by preventing contamination, and increase overall production efficiency.
- Q: What types of materials are typically moved by conveyors in this section? A: Raw EVA pellets/granules, various additives (fillers, pigments, stabilizers, cross-linking agents), recycled EVA, and finished EVA compound granules/sheets/pellets.
- Q: Are conveyor systems custom-designed or off-the-shelf for EVA applications? A: Often a combination. While standard conveyor types exist, their specific configuration, material, and controls are usually custom-designed to fit the unique layout, material properties, and capacity requirements of an EVA plant.
- Q: What are the main benefits of using conveyor machines over manual handling in EVA production? A: Increased speed, reduced labor, improved ergonomics, enhanced safety, less material waste, better process control, and higher throughput.
Types of Conveyors & Their Applications
- Q: What are the most common types of conveyor machines used in EVA chemical and compounding? A: Belt conveyors, screw conveyors, pneumatic conveyors (dilute and dense phase), vibratory conveyors, and sometimes bucket elevators.
- Q: Where are belt conveyors typically used in EVA compounding? A: For transporting large volumes of bulk EVA pellets or finished compound granules over long distances, or for feeding extruders/mixers with a consistent flow.
- Q: What is a screw conveyor and how is it used with EVA materials? A: A screw conveyor (or auger conveyor) uses a rotating helical screw blade within a tube or trough to move granular or powdered EVA materials, often used for precise feeding of additives or transferring materials vertically or horizontally over shorter distances.
- Q: When would pneumatic conveyors be preferred for EVA materials? A: For transporting fine powders (like fillers or pigments) or small pellets over long distances, especially if the path is complex or involves multiple elevation changes. They are also good for enclosed, dust-free transfer.
- Q: What is the difference between dilute phase and dense phase pneumatic conveying for EVA? A: Dilute phase uses high air velocity and low material concentration, suitable for light, fine powders. Dense phase uses lower air velocity and higher material concentration, ideal for abrasive or fragile materials, reducing wear and material degradation.
- Q: Are vibratory conveyors used in EVA compounding? If so, where? A: Yes, they are used for precise, controlled feeding of small quantities of additives, for screening or spreading materials, or for short-distance horizontal transport where gentle handling is required.
- Q: Can conveyors handle both raw EVA pellets and fine additive powders? A: Yes, but different types of conveyors are optimized for each. Belt conveyors for pellets, screw or pneumatic for powders.
- Q: How are conveyors used to feed the main mixers or extruders in an EVA plant? A: Often, belt conveyors or screw conveyors are used to deliver bulk EVA pellets, while screw conveyors or pneumatic systems precisely meter in various additives.
- Q: What role do conveyors play in the cooling and pelletizing section? A: They transport the hot extruded EVA strands or sheets through cooling baths/tunnels and then carry the cooled material to the pelletizer or shredder, and finally move the finished pellets to storage.
- Q: Are conveyors used for packaging EVA compounds? A: Yes, after pelletizing, conveyors often transport the finished EVA pellets to bagging machines, bulk bag fillers, or storage silos.
Design Considerations & Material Handling
- Q: What factors influence the selection of a conveyor type for a specific EVA application? A: Material properties (abrasiveness, stickiness, particle size, bulk density), required throughput, distance, elevation changes, footprint, environmental conditions, and budget.
- Q: How do material properties of EVA and its additives affect conveyor design? A: Abrasive fillers require wear-resistant components. Sticky materials need non-stick surfaces and easy cleaning. Fine powders demand enclosed systems to prevent dust.
- Q: What are common materials of construction for conveyors handling EVA? A: Stainless steel (especially for hygiene or corrosive additives), carbon steel (for general bulk EVA), and specific wear-resistant plastics for belts or liners.
- Q: How do you prevent contamination of EVA compounds during conveying? A: Using enclosed systems (pneumatic, screw conveyors), choosing appropriate materials of construction, ensuring easy cleaning, and sometimes employing dedicated lines for specific compounds.
- Q: What measures are taken to minimize dust generation during EVA material conveying? A: Enclosed systems, dust collection hoods at transfer points, proper belt speeds, and careful design of chutes and hoppers.
- Q: How do conveyor systems handle different formulations or color changes in EVA production? A: Dedicated lines for critical products, or systems designed for quick and thorough cleaning (e.g., easy-access screw conveyors, clean-in-place features for pneumatic lines).
- Q: What is the importance of conveying speed in EVA compounding? A: It directly impacts throughput and material degradation. Too fast can cause attrition, too slow can reduce efficiency. It must be synchronized with upstream and downstream processes.
- Q: How are transfer points designed to optimize material flow and minimize spillage? A: Proper chute angles, enclosed transfer chutes, impact beds under drop points for belt conveyors, and integrated dust collection systems.
- Q: What role do sensors and controls play in conveyor systems for EVA? A: Sensors (level, speed, position) monitor material flow and conveyor operation, while controls automate start/stop, regulate speed, and integrate with the overall plant control system (PLC/DCS) for seamless operation.
- Q: How are bulk bags or silos unloaded into conveyor systems? A: Bulk bag dischargers with integrated hoppers and feeders (screw or vibratory) feed into the main conveyor lines. Silos typically use rotary valves or vibratory dischargers at their base.
Safety & Maintenance
- Q: What are the primary safety concerns associated with conveyor machines in an EVA plant? A: Pinch points, entanglement hazards, falling material, dust explosions (with certain additives), and unauthorized access to moving parts.
- Q: What safety features are commonly integrated into EVA conveyor systems? A: Emergency stop buttons/pull cords, safety guarding, lockout/tagout procedures, belt misalignment switches, speed sensors, and dust explosion prevention systems (if applicable).
- Q: How is dust explosion risk managed when conveying certain EVA additives? A: Using ATEX-certified equipment (explosion-proof motors, sensors), inert gas purging in enclosed systems, dust collection with explosion vents, and proper grounding to prevent static discharge.
- Q: What kind of maintenance do conveyor machines in an EVA section require? A: Regular lubrication, belt tensioning/tracking, cleaning, inspection of wear parts (belts, idlers, screws, bearings), motor checks, and calibration of sensors.
- Q: How does proper maintenance impact the lifespan and efficiency of conveyors? A: It extends their operational life, prevents breakdowns, maintains consistent material flow, reduces energy consumption, and ensures continued product quality.
- Q: Are there specific cleaning procedures for conveyors when switching between different EVA formulations? A: Yes, this can range from simple brushing and vacuuming to full wash-downs or even purging with a sacrificial material, depending on the contamination sensitivity of the new formulation.
- Q: What are common wear parts on conveyor systems in EVA compounding? A: Conveyor belts, idlers, bearings, screw flights, pipe elbows (for pneumatic), and rotary valves.
- Q: How do extreme temperatures (hot EVA) affect conveyor design and material choice? A: High-temperature resistant belts or components are required for hot materials. Cooling sections are often integrated before conveying to prevent material stickiness or damage to the conveyor.
- Q: What is the role of interlocks between conveyors and other equipment? A: Interlocks ensure that conveyors only operate when upstream and downstream equipment is ready, preventing material bottlenecks, spills, and equipment damage.
- Q: How do you troubleshoot common conveyor issues like belt tracking or material buildup? A: Belt tracking issues require idler adjustment or re-splicing. Material buildup requires regular cleaning, proper chute design, and sometimes specialized belt scrapers or air cannons.
Advanced & Future Trends
- Q: Are there any “smart” conveyor systems used in EVA production? A: Yes, with integrated sensors for real-time monitoring of material flow, weight, and even quality parameters. These data can be fed into a central control system for optimization.
- Q: How do conveyors contribute to overall plant automation in EVA manufacturing? A: By providing continuous, automated material movement, they are a fundamental component of a highly automated plant, reducing manual intervention and enabling lights-out operation in some areas.
- Q: Can conveyors be integrated with robotic systems in EVA compounding? A: Yes, robots can be used for tasks like de-palletizing raw materials onto conveyors, or for picking and placing finished products from conveyors onto packaging lines.
- Q: What is the environmental impact of conveyor usage in EVA production? A: Efficient conveyors reduce energy consumption compared to manual transport, minimize material waste, and can be designed for lower noise levels.
- Q: How do energy efficiency considerations influence conveyor design for EVA? A: Using high-efficiency motors, optimizing belt speeds, minimizing friction, and using regenerative drives for decline conveyors can all contribute to energy savings.
- Q: Are there any trends towards more sustainable conveyor solutions for EVA? A: Focus on longer-lasting components, energy-efficient designs, reduced noise pollution, and potentially using recycled materials in conveyor construction where appropriate.
- Q: How does the “Industry 4.0” concept apply to conveyor systems in EVA plants? A: Integration with IoT sensors, data analytics for predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and autonomous operation through AI-driven control systems.
- Q: What innovations are emerging in conveyor technology relevant to EVA? A: Modular designs for easier reconfiguration, advanced sensor technology for material tracking and quality control, and more energy-efficient and quieter drives.
- Q: How do conveyors facilitate traceability of EVA compounds? A: By controlling material flow and allowing for batch tracking through integrated weighing and barcode/RFID scanning systems at various points.
- Q: What is the role of flexible conveying systems (e.g., tube chain conveyors) in EVA? A: They are excellent for enclosed, dust-free transport of powders and granules, particularly where multiple inlets/outlets are needed or where the path is complex and space is limited.
- Q: How do conveyors handle “off-spec” or recycled EVA material? A: Often, dedicated conveyor lines or specific sections are used to transport and process recycled or off-spec material back into the production stream or to a separate collection area.
- Q: What considerations are there for conveying EVA materials that might generate static electricity? A: Using anti-static belts, proper grounding of all metallic components, and sometimes incorporating ionizing bars or humidification to dissipate static charges.
- Q: How do conveyor systems contribute to overall plant layout and space optimization? A: They can be designed to fit into tight spaces, go over/under existing equipment, and efficiently connect different processing units, leading to a more compact and logical plant layout.
- Q: What is the lifespan of a typical conveyor system in an EVA compounding environment? A: With proper maintenance and design, a well-built conveyor system can last 15-25 years or even longer, though wear parts will require regular replacement.
- Q: In what ways do conveyor machines improve the overall efficiency of an EVA chemical and compounding operation? A: By ensuring continuous, automated, and controlled material flow, reducing manual labor, minimizing downtime due to material handling issues, and enabling higher production rates.
Role of Machines and Sections in EVA Compounding
This section addresses common questions about the function of various machines and sections involved in the compounding of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) materials.
General Compounding & EVA Basics
- Q: What is EVA Compounding?
- A: EVA compounding is the process of mixing Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate polymer with various additives (like fillers, colorants, foaming agents, cross-linking agents, etc.) to achieve specific properties for a final product.
- Q: Why is Compounding necessary for EVA?
- A: Compounding is crucial to enhance EVA’s properties such as strength, flexibility, color, UV resistance, flame retardancy, and most importantly, to enable foaming for products like footwear soles or mats.
- Q: What are some common applications of compounded EVA?
- A: Footwear soles, foam mats, insulated wire and cable, hot melt adhesives, solar panel encapsulants, and flexible packaging films.
Hopper
- Q: What is the primary role of the Hopper in an EVA compounding line?
- A: The Hopper is a large funnel-shaped container used for storing and feeding raw materials (EVA pellets, additives in powder or pellet form) into the extruder in a controlled manner.
- Q: What types of materials are typically fed into the Hopper?
- A: Virgin EVA pellets, masterbatches (color, additive), fillers (e.g., calcium carbonate, talc), foaming agents, cross-linking agents, and other performance enhancers.
- Q: Are there different types of Hoppers?
- A: Yes, they can range from simple gravity-feed hoppers to more sophisticated agitated or vacuum hoppers, especially for difficult-to-flow or hygroscopic materials.
- Q: How does the Hopper ensure consistent feeding?
- A: Many hoppers are equipped with agitators or vibrators to prevent bridging of material and promote uniform flow into the feeding throat of the extruder. Load cells can also be used for gravimetric feeding control.
Screw Barrel
- Q: What is the Screw Barrel assembly?
- A: The Screw Barrel is the heart of the extruder. It consists of a long, heated cylindrical barrel housing one or more rotating screws, which convey, melt, mix, and homogenize the polymer mixture.
- Q: What are the main functions of the Screw in an EVA extruder?
- A:
- Conveying: Moving raw materials from the hopper to the die.
- Melting: Generating shear heat and heat transfer from the barrel to melt the polymer.
- Mixing: Blending the polymer with additives to achieve homogeneity.
- Devolatilization (sometimes): Removing trapped gasses or moisture.
- Pressurizing: Building pressure to force the molten material through the die.
- A:
- Q: How does the Screw Barrel facilitate melting of EVA?
- A: The combination of external heating zones on the barrel and mechanical shear energy generated by the rotating screw against the barrel wall and the material itself causes the EVA pellets to melt into a viscous fluid.
- Q: Why are there different zones in a Screw (e.g., feed, compression, metering)?
- A: Each zone serves a specific purpose:
- Feed Zone: Conveys solid pellets.
- Compression Zone: Melts and compacts the material, removing air.
- Metering Zone: Homogenizes the melt and builds pressure for extrusion.
- A: Each zone serves a specific purpose:
- Q: What is the importance of L/D ratio in a Screw Barrel?
- A: The Length-to-Diameter (L/D) ratio affects residence time, mixing efficiency, and melting capacity. A higher L/D generally allows for better mixing and melting.
- Q: Why is temperature control critical in the Screw Barrel for EVA?
- A: Precise temperature control prevents degradation of EVA (which can occur at high temperatures) and ensures optimal melt viscosity for processing and good mixing of additives, especially heat-sensitive ones like foaming agents.
Extruder
- Q: What is an Extruder in the context of EVA compounding?
- A: An extruder is a machine that processes polymeric materials by melting and forcing them through a die to create a continuous profile or pelletized strands. In compounding, it’s primarily used for mixing and homogenization.
- Q: What are the two main types of extruders used for EVA compounding?
- A:
- Single-Screw Extruders: Simpler, good for basic mixing and high throughput.
- Twin-Screw Extruders (Co-rotating or Counter-rotating): Offer superior mixing, devolatilization, and compounding capabilities for complex formulations due to intermeshing screws. Twin-screw extruders are more common for high-quality EVA compounding.
- A:
- Q: How does an extruder ensure uniform mixing of EVA and additives?
- A: The design of the screw elements (mixing sections, kneading blocks in twin-screw extruders) generates high shear forces and distributive mixing, ensuring a homogeneous blend of all components within the molten EVA.
- Q: What is the “die head” of an extruder, and what is its purpose in compounding?
- A: The die head is the final part of the extruder where the molten, compounded EVA exits. In a compounding line, it typically forms strands or a sheet, which will then be cooled and pelletized.
Cutter (Pelletizer)
- Q: What is the role of the Cutter (Pelletizer) in the EVA compounding line?
- A: The Cutter, or Pelletizer, takes the continuous strands or sheet of compounded EVA emerging from the extruder die and cuts them into uniform pellets.
- Q: Why are EVA materials pelletized after compounding?
- A: Pellets are the preferred form for subsequent processing (e.g., injection molding, extrusion, or compression molding) because they are easy to handle, store, transport, and feed into other processing machinery. Uniform pellet size also aids consistent downstream processing.
- Q: What are the common types of pelletizers for EVA?
- A:
- Strand Pelletizers: Molten strands are cooled in a water bath and then fed into a rotating cutter.
- Underwater Pelletizers: Molten polymer is cut directly at the die face in a water-filled chamber, leading to spherical pellets.
- Die Face Pelletizers (Hot Cut): Similar to underwater but the cutting happens in air or with water spray, typically for specific applications.
- A:
Blower
- Q: What is the primary function of the Blower in an EVA compounding line?
- A: Blowers are primarily used to convey the freshly cut EVA pellets, often from the pelletizer to a cooling system (like a vibratory screen or fluidized bed) and then to storage silos or packaging.
- Q: How does a Blower move the pellets?
- A: They create an airflow (pneumatic conveying) that entrains the pellets, moving them through ducts or pipes. This is a gentle way to transport pellets without causing much damage.
Vibrator (Vibratory Screen/Conveyor)
- Q: What is the role of a Vibrator (Vibratory Screen or Conveyor) in EVA pellet processing?
- A: Vibrators are often used for:
- Cooling: Spreading hot pellets to enhance airflow for more efficient cooling.
- Dewatering: Removing surface water from pellets that have been cooled in a water bath.
- Sizing/Screening: Separating oversized, undersized, or agglomerated pellets from the good product.
- A: Vibrators are often used for:
- Q: How does a Vibratory Screen cool EVA pellets?
- A: The vibrating motion spreads the pellets into a thin, uniform layer, increasing their surface area exposure to air (often forced air), facilitating rapid heat dissipation.
Conveyor Machine
- Q: What is the general purpose of Conveyor Machines in an EVA compounding plant?
- A: Conveyor machines are used for efficient and automated material handling, transporting raw materials to hoppers, intermediate products between processing stages, and finished pellets to storage or packaging.
- Q: What types of Conveyors are typically used?
- A:
- Belt Conveyors: For bulk raw materials or large volumes of pellets.
- Screw Conveyors (Augers): For powders or granular materials, often used for feeding specific additives.
- Pneumatic Conveyors (using Blowers): For clean, efficient transport of pellets over distances.
- Vibratory Conveyors: For controlled feeding, spreading, or gentle transport while aiding cooling or dewatering.
- A:
EVA Chemical & Compounding Section (Overall Process)
- Q: What happens in the “EVA Chemical” aspect of the section?
- A: This refers to the specific chemical properties of EVA, the selection of appropriate grades (based on VA content), and the careful choice and proportioning of various chemical additives that will be compounded with it to achieve desired end-product characteristics.
- Q: Why is the “Compounding Section” considered critical?
- A: It’s where all the raw materials come together and are transformed into a homogeneous, melt-blended material with the desired physical and chemical properties. The quality of compounding directly impacts the performance of the final EVA product.
- Q: What are some key parameters monitored in the EVA Compounding Section?
- A: Temperature profiles (barrel, die), screw speed, throughput, melt pressure, motor amperage, additive feed rates, and pellet quality (size, shape, consistency).
- Q: How does quality control fit into the EVA Compounding Section?
- A: In-process quality checks (e.g., melt flow index, density, visual inspection) are crucial. Samples are often taken for laboratory analysis to ensure the compounded material meets specifications before downstream processing.





















































































.jpg?w=218&resize=218,150&ssl=1)